USE:
The Object Definition contains paramaters such as name of the tested service interface and it's namespace allowing IFTT to locate the XML message on the middleware platform
in order to store it inside of the IFTT repository for further comparison. Below it is presented how to create a new object definition for PI inbound interface, PI outbound interface, synchronous interface, IDOC inbound / outbound interfaces, and AIF interfaces
In General Settings section you will find how to use already existing objects configuration for a newly created object, or how to configure IFTT in order to test data on remote ERP systems.
PI INBOUND / OUTBOUND / SYNCHRONOUS INTERFACE:
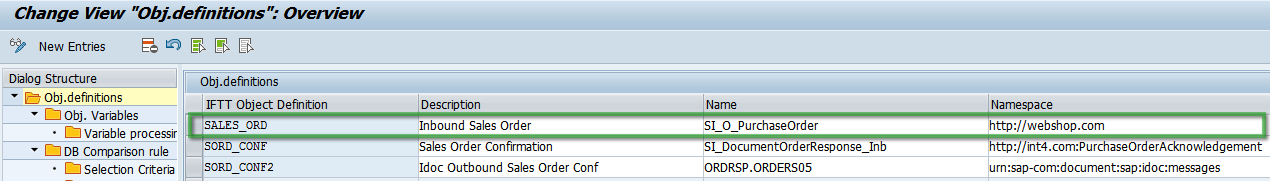
- Enter object definition ID and description.
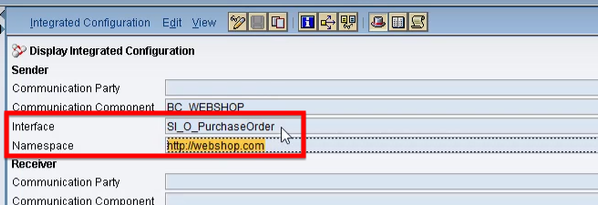
- Enter PI/PO service interface name and namespace.
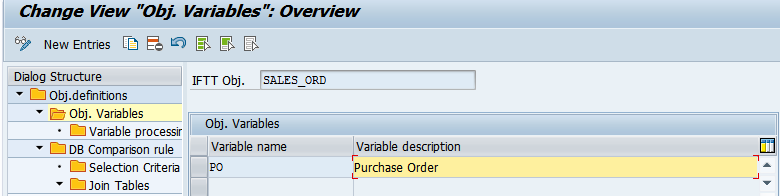
You can copy them from the ICO of the configured interface: - Define an unlimited number of variables and add a meaningful description for each of them.
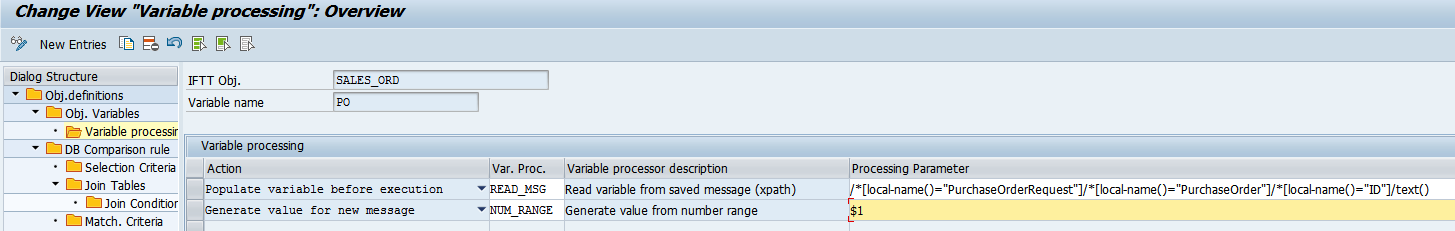
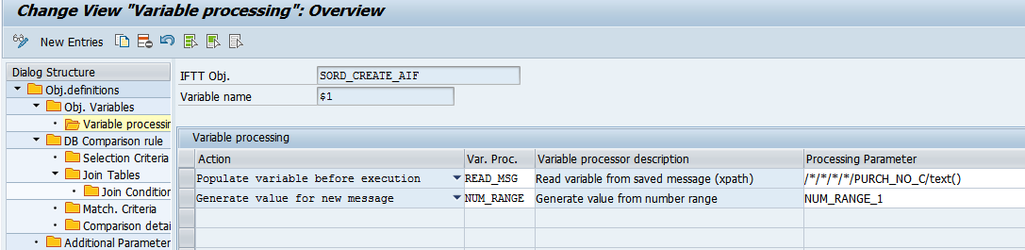
- For each of the variables define actions and define the processing that will be performed. For each action select one of variable processors and provide the processing parameter: This way variables can be used i.e.
- to identify documents to be compared,
- for creating new values from a number range for a newly created messages,
- for passing values to variables in next test cases.
IDOC INBOUND / OUTBOUND INTERFACE:
- Enter object definition ID and description.
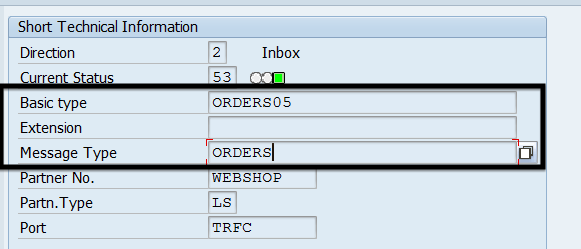
- Provide IDOC interface details in the Name field.
Name of IDOC interface is a combination of IDOC message type, basic type and an extension separated by dot (.).- In order to provide the correct information open relevant segments of the IDOC:
- for message type: /IDOC/EDI_DC40/MESTYP
- for basic type: /IDOC/EDI_DC40/IDOCTYP
- for extension: /IDOC/EDI_DC40/IDOCTYP
- The name of the interface is the combination of full Namespace, and six first letters of Interface Name separated by a dot: ' . ' .
Example:
For the IDOC with Basic Type ORDERS05, message type: ORDERS and no extension the interface name will be ORDERS.ORDERS05
- In order to provide the correct information open relevant segments of the IDOC:
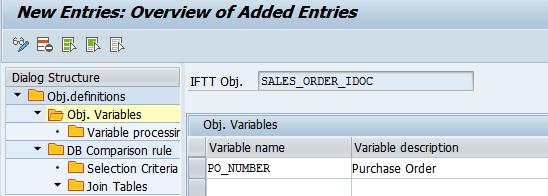
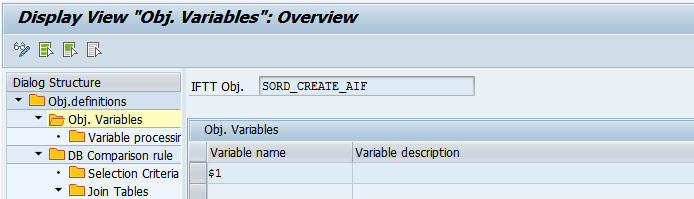
- Define an unlimited number of variables and add a meaningful description for each of them.
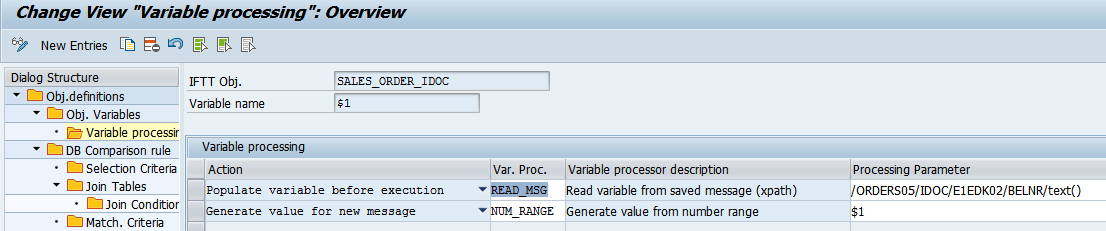
- For each of the variables define actions and define the processing that will be performed. For each action select one of variable processors and provide the processing parameter: This way variables can be used i.e.
- to identify documents to be compared,
- for creating new values from a number range for a newly created messages,
- for passing values to variables in next test cases.
AIF INTERFACE
USE:
The Object Definition contains parameters, such as generated name of the tested AIF interface allowing IFTT to locate the XML message in the AIF persistance on ECC. Thanks to this it is possible to store AIF XML message inside of the IFTT repository for further comparison.
- Enter object definition ID and description.
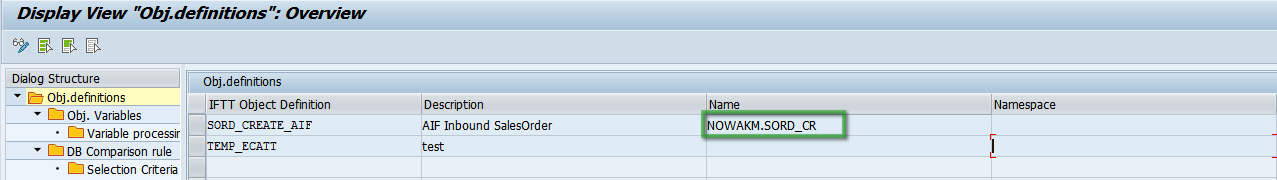
- Provide AIF interface details in Name field.
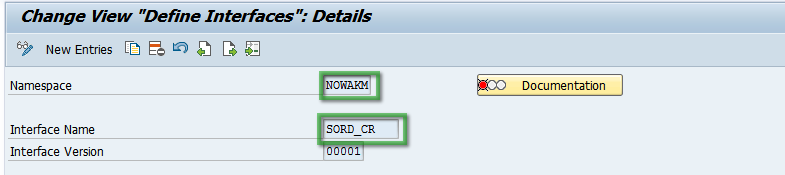
Name of AIF interface is a combination of an AIF Namespace and the first six letters of an AIF interface.- In order to provide correct information go to transaction /n/AIF/CUST
- Open branch: SAP AIF → Interface Development → Define Interface
- Open specific namespace and then open interface you want to test in IFTT
- The name of the interface is the combination of full Namespace, and six first letters of Interface Name separated by dot (.).
Example:For NOWAKM namespace and SORD_CR interface name - the name of the interface should be NOWAKM.SORD_C - Define an unlimited number of variables and add a meaningful description for each of them.
For each of the variables define actions and define the processing that will be performed. For each action select one of variable processors and provide the processing parameter: This way variables can be used i.e.- to identify documents to be compared,
- for creating new values from a number range for a newly created messages,
- for passing values to variables in next test cases.
GENERAL SETTINGS
- (OPTIONAL) Reference Object Definition ID can be entered in order to use configuration of another object definition.
- (OPTIONAL) If IFTT is installed on a remote system and it is intended to use documents from another system Ref. RFC Destination and Res. RFC Destination are required.
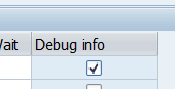
- In order to receive additional debugging details select Debug Info as active while configuring a new object. Debugging details will be available at the results screen
during the test case execution.